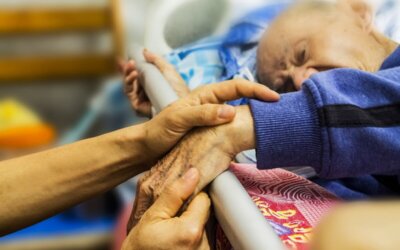
Advance care planning plays a crucial role in ensuring that patients’ end-of-life preferences are respected and carried out in hospice settings. It is a process that involves communication, documentation, and collaboration among patients, their loved ones, and healthcare professionals. To effectively implement advance care planning, it is important to consider certain essential steps that promote patient autonomy, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity.
Advance care planning plays a crucial role in ensuring that patients’ end-of-life preferences are respected and carried out in hospice settings. It is a process that involves communication, documentation, and collaboration among patients, their loved ones, and healthcare professionals. To effectively implement advance care planning, it is important to consider certain essential steps that promote patient autonomy, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity.
Step 1: Engage in Open and Honest Conversations
Effective advance care planning begins with open and honest conversations between patients, their families, and healthcare professionals. It is important to create a comfortable and non-judgmental environment where patients feel free to express their thoughts, concerns, and preferences about their end-of-life care.
Step 2: Understand Patient Values and Preferences
Understanding the values, beliefs, and preferences of patients is a critical aspect of advance care planning. Healthcare professionals should be attentive to the patient’s cultural and religious background, as well as their personal experiences and expectations. This understanding is essential for fostering cultural sensitivity and inclusivity throughout the planning process.
Step 3: Identify Healthcare Decision-Makers
Patients should designate a healthcare decision-maker, also known as a healthcare proxy or power of attorney, who will make decisions on their behalf in the event they become unable to communicate their preferences. This person should be someone the patient trusts and who understands their values and wishes.
Step 4: Document Patient Preferences
Once the patient’s preferences are understood, they should be documented in an advance directive, such as a living will or a durable power of attorney for healthcare. This document provides a clear, legally-binding record of the patient’s wishes, which healthcare professionals can refer to when making treatment decisions.
Step 5: Regularly Review and Update Advance Directives
Advance directives should be reviewed and updated periodically to ensure they remain accurate and reflective of the patient’s current preferences. Changes in the patient’s health, personal circumstances, or evolving beliefs may necessitate modifications to their advance care plan.
Step 6: Communicate Advance Directives with Relevant Parties
Patients, their families, and healthcare professionals should all be aware of the advance directive and its contents. This ensures that everyone involved in the patient’s care is informed about the patient’s preferences and can work together to honor those wishes.
Step 7: Implement Advance Care Planning Across the Care Continuum
Advance care planning should be integrated into the overall care plan for patients receiving hospice care. This includes incorporating the patient’s preferences into care assessments, care plans, and interdisciplinary team meetings. By doing so, healthcare professionals can ensure that the patient’s end-of-life care aligns with their values and preferences, fostering a sense of autonomy and dignity.
Effective advance care planning involves open communication, understanding patient values, designating decision-makers, documenting preferences, and implementing the plan across the care continuum. By following these essential steps, healthcare professionals can provide culturally sensitive and inclusive hospice care that respects patient autonomy and honors their end-of-life wishes.